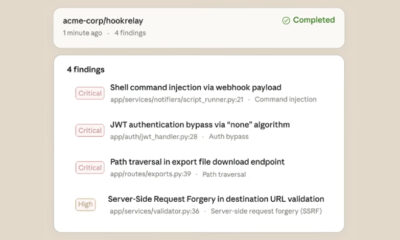
A critical security vulnerability in the OpenClaw software has been patched, the project’s maintainers announced. The flaw, which received a high severity rating, could have allowed an attacker to execute arbitrary code on a user’s system simply by having them click a specially crafted link.
The issue has been assigned the identifier CVE-2026-25253. It carries a CVSS score of 8.8, indicating a high level of risk. The vulnerability was addressed in OpenClaw version 2026.1.29, which was released to the public on January 30, 2026.
Nature of the Vulnerability
Security researchers classified the flaw as a token exfiltration vulnerability. This type of weakness can enable an attacker to steal authentication tokens or other sensitive data. In this specific case, the exfiltrated information could be leveraged to achieve remote code execution, granting an attacker control over the affected system.
The attack vector required minimal user interaction. A potential victim would only need to click a malicious link, potentially delivered via email, instant message, or a compromised website. No further actions would be necessary for the exploit to potentially succeed.
Software Background and Impact
OpenClaw is software known in certain online communities, previously referred to under names such as Clawdbot and Moltbot. Its specific functions vary, but software of this nature often operates within messaging platforms or online services. The disclosure highlights that security risks can exist in a wide range of tools used by individuals and organizations.
While the exact number of affected users is not specified, the public disclosure of the vulnerability underscores the importance of prompt software updates. Systems running versions of OpenClaw prior to 2026.1.29 remain potentially vulnerable to exploitation if the patch is not applied.
Response and Remediation
The maintainers of OpenClaw resolved the security hole in the late January update. The standard mitigation for all users is to immediately update their software to the latest patched version, 2026.1.29 or later. This action is considered the primary and most effective defense against potential attacks exploiting this flaw.
Security professionals routinely advise users to exercise caution with unsolicited links, regardless of their source. This incident serves as a practical reminder of that general security principle, as the exploit was triggered by a simple link click.
There have been no widespread reports of active exploitation of CVE-2026-25253 in the wild at the time of the patch release. However, the publication of technical details often prompts malicious actors to develop their own exploit code, making timely updates crucial.
Looking Ahead
Users and administrators of OpenClaw are expected to prioritize the installation of the updated version. The cybersecurity community will likely monitor threat intelligence feeds for any signs that this vulnerability is being used in active attack campaigns. Further technical analysis of the patch may be published by independent security researchers in the coming days, providing a deeper understanding of the underlying code defect.
Source: Based on original security disclosure