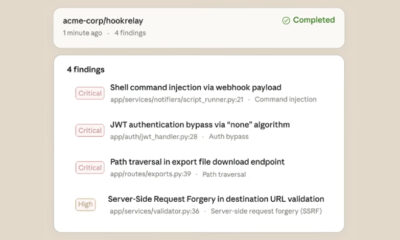
Cybersecurity researchers have identified a new malicious package on the npm registry that presents itself as a legitimate WhatsApp Application Programming Interface (API). The package, named lotusbail, was first uploaded by an anonymous user and has been downloaded more than 56,000 times. It allows attackers to intercept every WhatsApp message, harvest contact lists, and capture login tokens, effectively linking the attacker’s device to the victim’s WhatsApp account.
Background
npm as a Distribution Platform
npm is the most widely used package manager for JavaScript and Node.js applications. It hosts millions of libraries that developers download and integrate into their projects. The platform’s openness facilitates rapid development but also creates opportunities for malicious actors to inject harmful code into the ecosystem.
WhatsApp API and Security Concerns
WhatsApp provides official APIs for business and developer use, enabling automated messaging and customer support. The APIs require authentication tokens that grant access to a user’s account. Compromise of these tokens can allow attackers to impersonate the user, read private conversations, and manipulate account settings.
Package Details
Name and Distribution
The package is publicly available under the name lotusbail. Since its first upload, it has accumulated more than 56,000 downloads across a variety of projects. The uploader is listed as an anonymous or pseudonymous user, with no publicly disclosed identity.
Malicious Functionality
Unlike legitimate WhatsApp API wrappers, lotusbail includes additional code that intercepts outgoing and incoming messages. It captures the content of every message, logs contact information, and records authentication tokens used to establish the WhatsApp connection. The package then forwards this data to an external command‑and‑control server controlled by the attacker.
Installation and Activation
Developers install the package via the npm command line. Once included in a Node.js application, the package initiates a background process that runs alongside the legitimate API calls. The malicious code is obfuscated, making it difficult for static analysis tools to detect the hidden payload.
Consequences for Users
Privacy Breaches
All messages sent or received through an application that incorporates lotusbail are exposed to the attacker. This includes personal, business, and group conversations. Sensitive attachments, such as documents or images, are also captured.
Account Compromise
The stolen login tokens allow the attacker to log into the victim’s WhatsApp account from a separate device. Once logged in, the attacker can read messages, add contacts, and potentially send messages that appear to come from the legitimate user.
Potential for Phishing and Fraud
With access to contact lists and conversation history, attackers can craft convincing phishing messages or fraudulent requests. They can also manipulate group chats or create fake business communications.
Reactions from the Community
Researchers’ Findings
Security researchers who uncovered the package released a detailed report outlining the code’s behavior and the extent of data exfiltration. The report included logs of intercepted messages and a timeline of token theft.
npm’s Response
Upon notification, npm’s security team temporarily removed the lotusbail package from the registry. The package remains unlisted, and npm has issued a warning to developers to audit their dependencies carefully. The vendor is also working with the Node.js community to improve automated scanning of packages for malicious code.
WhatsApp’s Position
WhatsApp has not released an official statement regarding the incident. The company’s security team is reportedly investigating potential impacts on the broader user base. No evidence suggests that the company’s core infrastructure was compromised.
Implications for Developers and the npm Ecosystem
Dependency Management Practices
The incident highlights the need for rigorous dependency reviews. Developers are encouraged to use tools that analyze package provenance, verify digital signatures, and monitor for known vulnerabilities.
Policy and Governance
npm may consider tightening its review process for packages that interact with external APIs, especially those that require authentication tokens. The incident also underscores the importance of community reporting mechanisms and timely removal of malicious code.
Broader Security Outlook
Malicious packages that masquerade as legitimate libraries are not new. This event serves as a reminder that supply‑chain attacks can target widely used platforms and that vigilance is required at every layer of software development.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Security teams are advised to audit any projects that may have incorporated lotusbail and to revoke any WhatsApp authentication tokens that were exposed. Developers should also update dependencies to the latest, verified versions of legitimate WhatsApp API libraries. npm will continue to monitor the registry for similar threats and may implement additional automated checks. The broader developer community remains watchful for further developments, and the incident may prompt revisions to dependency management policies across the industry.