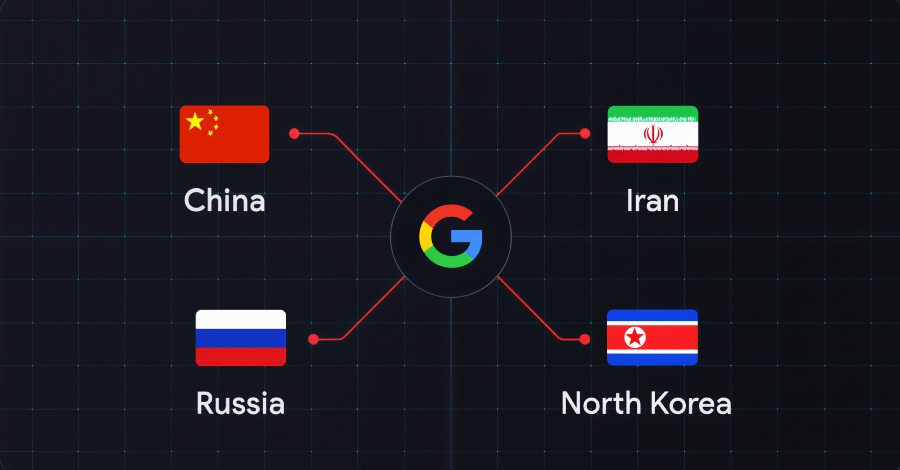
state-sponsored hacking groups from China, Iran, North Korea, and Russia are conducting coordinated cyber operations targeting the global defense industrial base. This assessment was published by the Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) in a recent report detailing sustained campaigns against defense contractors and suppliers.
The tech giant’s threat intelligence division stated that the adversarial targeting is centered on four key themes. These include intelligence gathering on military capabilities, stealing technological secrets, disrupting supply chains, and pre-positioning for potential future disruptive attacks.
Scope and Attribution of the Campaigns
According to the findings, the campaigns are not isolated incidents but represent a persistent, global threat to national security infrastructure. The report attributes the activity to advanced persistent threat (APT) groups known to operate on behalf of the named nations’ governments.
These actors employ sophisticated techniques to infiltrate networks of companies involved in manufacturing weapons systems, developing military software, and providing logistical support to armed forces. The targeting is described as deliberate and strategic, focusing on entities that form the backbone of defense capabilities for numerous countries.
Methods and Motivations
While the full technical details of the attacks are classified within the report, Google indicated the use of phishing, exploitation of software vulnerabilities, and supply chain compromises. The primary motivation across all identified groups appears to be espionage, aimed at closing technological gaps and gaining strategic military advantages.
The theft of intellectual property, such as blueprints for advanced equipment or proprietary software code, can provide significant economic and tactical benefits. Furthermore, understanding an adversary’s supply chain can reveal critical weaknesses and dependencies.
Industry and Security Implications
The persistent targeting of the defense industrial base poses a direct challenge to global security. Successful breaches can undermine the technological edge of nations and potentially compromise the integrity of military systems. This activity forces defense contractors to allocate substantial resources toward cybersecurity, increasing the cost of developing new technologies.
Security experts note that these campaigns blur the line between traditional espionage and preparation for conflict in the digital domain. The pre-positioning of malware within critical infrastructure is particularly concerning, as it could be activated to cause disruption during geopolitical tensions.
Ongoing Response and Future Outlook
Google’s report is part of a broader effort by cybersecurity firms and government agencies to expose and counter state-sponsored cyber activity. The disclosure aims to bolster defenses within the targeted sector by providing indicators of compromise and detailing the tactics of the adversary groups.
Moving forward, the Google Threat Intelligence Group and other security organizations are expected to continue monitoring these campaigns closely. Further public disclosures and technical advisories are likely as new attack methods are identified. Defense contractors worldwide are anticipated to face continued pressure to harden their networks against these advanced, state-backed threats, with increased collaboration between the private sector and government defense agencies seen as a critical next step.
Source: Google Threat Intelligence Group