A Brazilian recruiter has successfully transitioned a LinkedIn-based initiative into a full-fledged business, aided by the rapid creation of a professional website using an artificial intelligence-powered builder. Tammy Silva reported constructing the digital hub in a single afternoon to manage the scaling demands of her operation.
Silva began sharing remote job opportunities and career advice on LinkedIn during the pandemic. After relocating to Brazil following years abroad, she identified a significant knowledge gap: many professionals in the country were unaware they could work remotely for U.S. companies and earn U.S. dollar salaries.
Her initial voluntary posts covered job openings, resume tips, and interview advice. This effort, which she initially undertook to help a small number of people, unexpectedly grew a substantial audience, leading to the establishment of a formal recruiting agency.
Business Growth and Operational Challenges
The project evolved into a multi-faceted business connecting Brazilian talent with U.S. startups. It now includes a large audience of job seekers, paid coaching sessions, speaking engagements, and a newsletter. Silva’s LinkedIn following exceeds 190,000 users.
Her operational model was based on providing free, ungated content and genuine assistance. However, the venture’s success introduced a significant administrative burden. Silva stated she received over 50 direct messages daily with repetitive inquiries about her services, creating what she described as an “inbox problem.”
The volume of communication made it difficult for potential clients to understand her offerings, necessitating a centralized information source. Silva acknowledged she had delayed creating a website for months due to other business priorities.
Rapid Website Development and Implementation
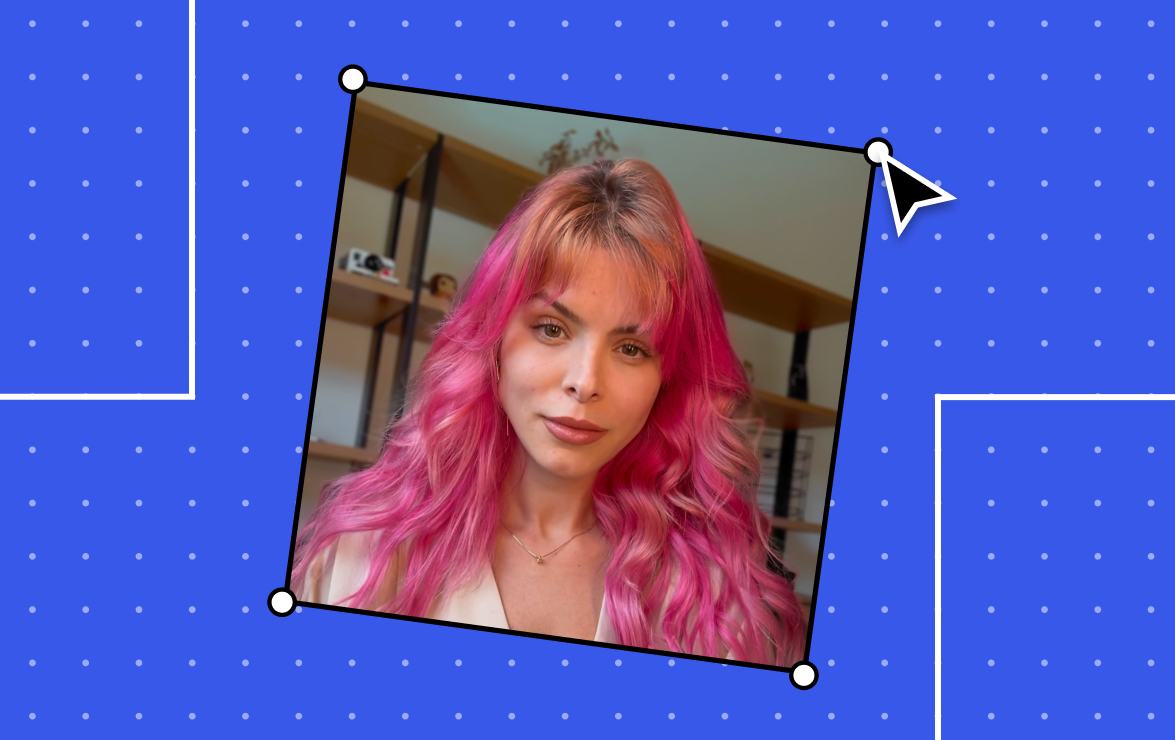
To solve the communication bottleneck, Silva used an AI website builder available on a popular web hosting platform. She completed the site, tammysilva.com.br, in one afternoon without hiring a designer or developer.
The process involved the AI tool generating a site structure aligned with her vision. She then used drag-and-drop editing blocks to customize the layout and refine the copy. The platform’s managed hosting service handled technical maintenance, including updates and security.
The website serves as a self-service hub, clearly explaining her services, separating free resources from paid offerings, collecting resumes into a candidate database, and driving newsletter signups. It features a distinctive pink color scheme consistent with her personal brand.
Measurable Outcomes Post-Launch
The website has produced tangible business results since its launch in August. Silva reported nearly 23,000 site visits, with monthly views exceeding 7,000 during peak periods.
More significantly, the platform has drastically reduced her inbound message volume. Potential clients now find information independently before contacting her. Her one-on-one coaching sessions were fully booked rapidly, with ten slots filling in two days without active promotion on social media.
“Now people already have all the information. They don’t need to message me to ask what I do,” Silva said.
Future Developments and Industry Context
Based on this experience, Silva is now building a second website for her B2B recruiting business using the same platform and method. The case highlights a growing trend where professionals leverage AI-assisted tools to quickly establish an online presence without deep technical expertise.
The platform she used combines an AI builder for initial creation with managed hosting to handle backend technical responsibilities, allowing business owners to focus on core operations. This approach is becoming increasingly common for entrepreneurs and small businesses seeking efficient digital infrastructure.
Silva’s story demonstrates how a social media initiative can be formalized and scaled through owned digital property. The website provides a controlled environment for business growth, independent of third-party algorithm changes on social platforms.
Source: Adapted from original case study